Jiakaicheng Wealth Center, Financial Third Street, Jiangsu Province, China
Home > Products >
Heating furnace spacer block
Working Temperature:1550 ℃
Compressive strength :4 Mpa under 1200 ℃ Suitable for High temperature , compressive and static environment
Heat-Resist supporting block Cobalt Alloy
- Order phone:+86-15320265364
- E-mail:jack@riverside-tech.cn
Detail
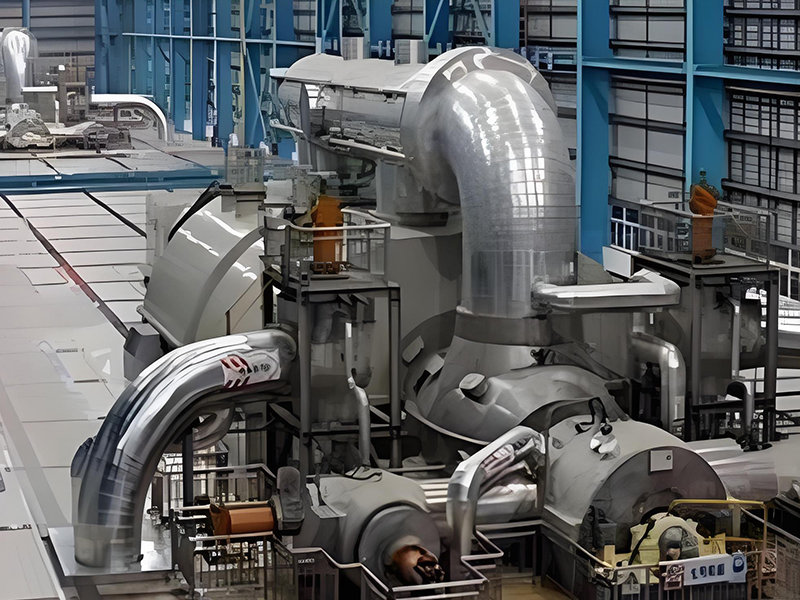
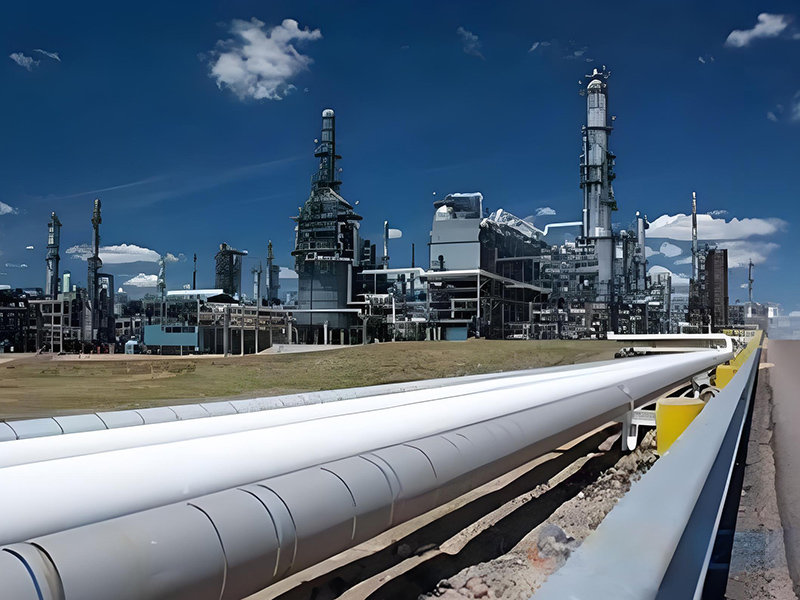
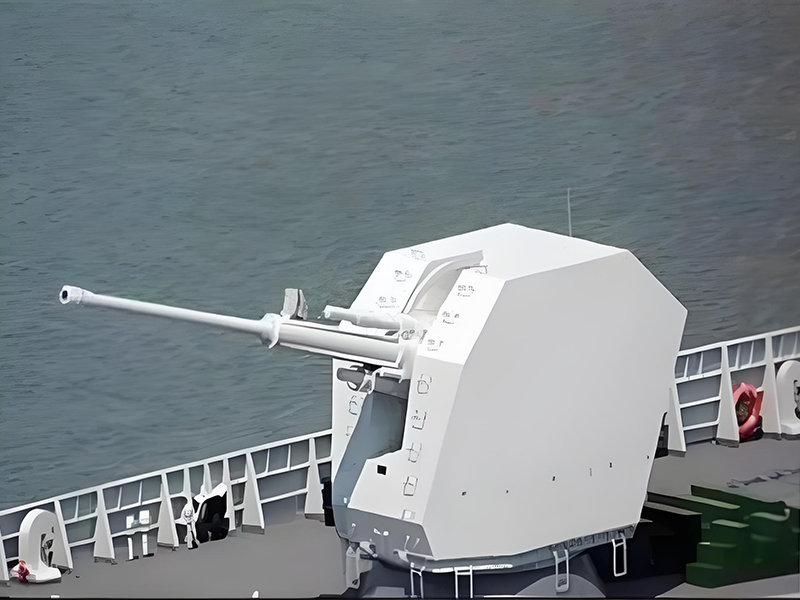



applied for supercritical boilers.applied for oil pipelines.applied for Millitary
Test and research show that metal glass has a melting point of up to 1,750°C and maintains exceptional compressive strength and oxidation resistance at 1,500°C. Table 1 contrasts the properties of cobalt - based and metal - glass spacer blocks, as detected by oxide layer crystalline phase analysis and high - temperature furnace testing. Thanks to its high - temperature strength and hardness, amorphous structure, and non - bonding with oxide scale, metal - glass spacer blocks are easy to clean and effectively prevent surface defects like lumps and blisters on steel billets caused by oxidized iron scales.
Table 1: Performance Comparison of Cobalt-based Spacer Blocks, Metal-glass Spacer Blocks, and Heating Furnace Spacer Blocks
Product Grade |
Density/
|
Melting
|
Oxidation
|
Maximum service
|
Maximum
|
Co50 |
8.2 | 1380 | 8.63 | 0.98 | 1350 |
Co40 |
8.2 | 1380 | 7.55 | 0.98 | 1350 |
Metallic Glass |
7.7 | 1750 | 2.21 | 4.41 | 1500 |
Heating furnace
|
7.388 | 1750 | 2.00 | 110.00 | 1550 |
In 2019, Yantai Best Furnace Tube Plant collaborated with Changchun University of Technology, Harbin Institute of Technology (Weihai), and Northeastern University. Building upon metallic glass, they developed a new high-temperature spacer block material named HHSW. This material is distinguished by its ability to withstand higher temperatures, maintain high hardness and strength-toughness, and exhibit superior wear resistance in high-temperature environments.
Tests (see Fig. 3 for the HHSW spacer block test report, dated July 2021) indicate that HHSW spacer blocks have a melting point of 1,750°C, with almost no plastic deformation before melting. Their maximum oxidation resistance temperature reaches 1,550°C. To date, their maximum compressive strength has increased to 110 MPa, with an impact toughness of 39.72 J/cm² , achieving near-zero damage.
Compared to metallic glass spacer blocks, HHSW blocks are less brittle and have higher compressive strength. They have been successfully used in multiple steel plants, including Shougang Qiansteel, Shandong Steel Rizhao, Baosteel Wuhan, and Anfeng Steel. After years of operation, inspections reveal no damage to the spacer blocks' appearance or geometry, with zero wear, as detailed in Table 2.
Table 2: Comparison of Spacer Block Wear
Product Grade |
Original height/mm |
Maximum furnace temperature/℃ |
Measured height/mm |
||
| 1 year | 2 year | 3 years | |||
Co50 |
110 | 1350 | 102 | 95 | 82 |
Co40 |
110 | 1350 | 101 | 93 | 79 |
Heating furnace
|
110 | 1420 | 110 | 110 | 108 |
Figure 3 Inspection Report of Heating Furnace Spacer Block
Sample Name |
Testing Item |
Testing Result |
Unit |
Testing Iethod |
HeatingfurnaceSpacerblock |
Density | 7.388 | g/cm³ | Drainage method |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion | 12.3449*10-6 | 1/K | GB/T 16535-2008 | |
| Melting point | No melting point was detected in the test range from room temperature to 1550℃ |
℃ | GB/T1425-1996 | |
| Oxidation resistance at 1200℃ | 0.01 | g/cm².h | Muffle furnace | |
| 0xidation resistance at 1300℃ | 0.02 | g/cm².h | Muffle furnace | |
| Oxidation resistance at 1350℃ | 0.02 | g/cm².h | Muffle furnace | |
| Indentation depth at 1250℃ under 0.5kg/mm²pressure |
0.04 | mM | High-temperature hardness tester |
|
| Indentation depth at 1300℃ under 0.5kg/mm²pressure |
0.05 | mM | High-temperature hardness tester |
|
| Indentation depth at 1350℃ under 0.5kg/mm²pressure |
0.05 | ITM | High-temperature hardness tester |
|
| Maximum applicable temperature | >1550 | ℃ | Laboratory method | |
| Maximum compressive strength at 1200℃ |
72 | MPa | Universal testing machine |
Figure 3 Inspection Report of Heating Furnace Spacer Block
The development of metal - glass spacer blocks, though solving many problems of traditional cobalt - based alloy ones,still has issues. The main problem is their fragility (solved in heating furnace spacer blocks),and they still use the straddle - clip installation method.
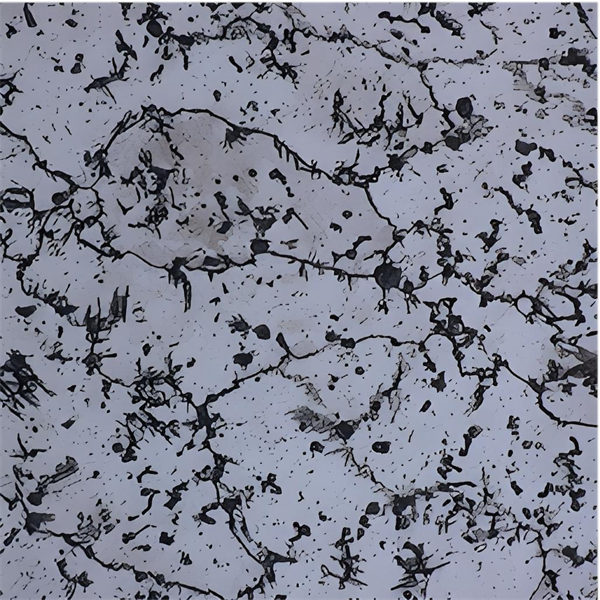

Figure 4 Metallographic Structure of Heating Furnace Spacer Block
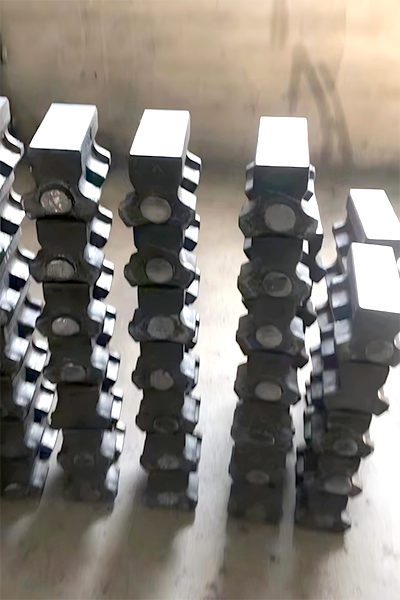
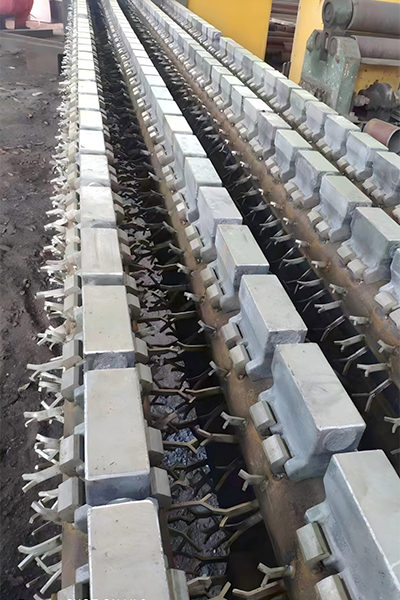
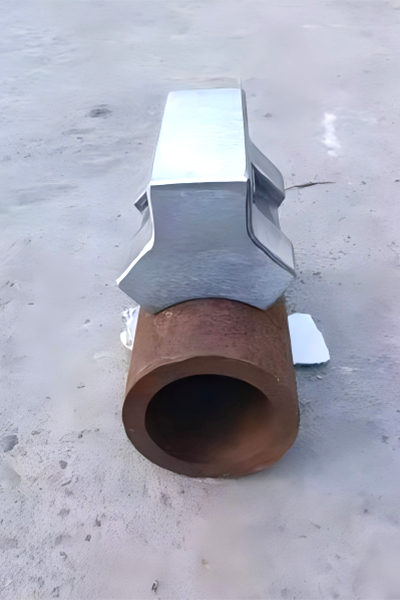
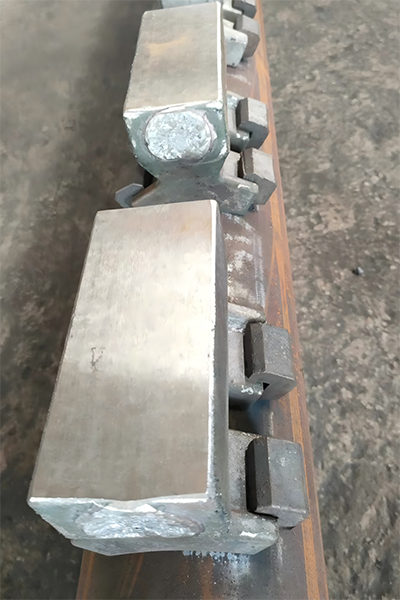




Figure 5 Product Images of Heating Furnace Spacer Block
Comparison Figure
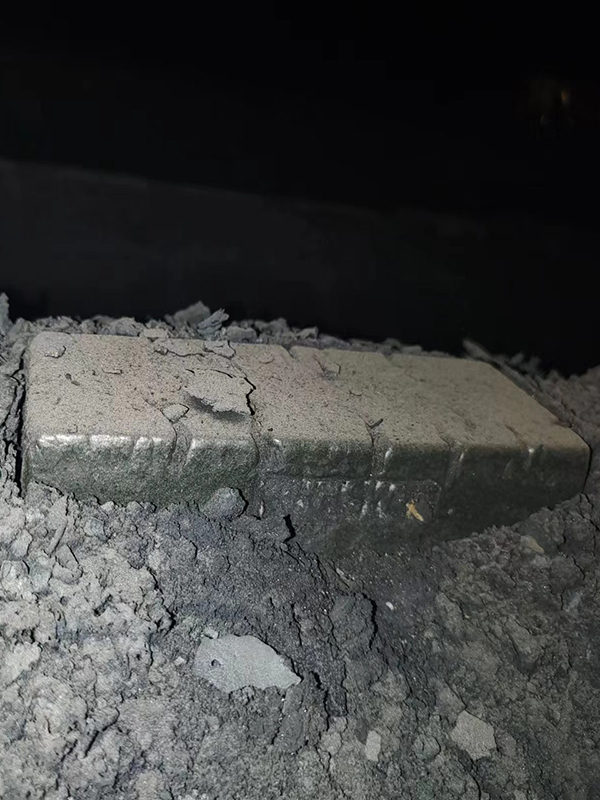
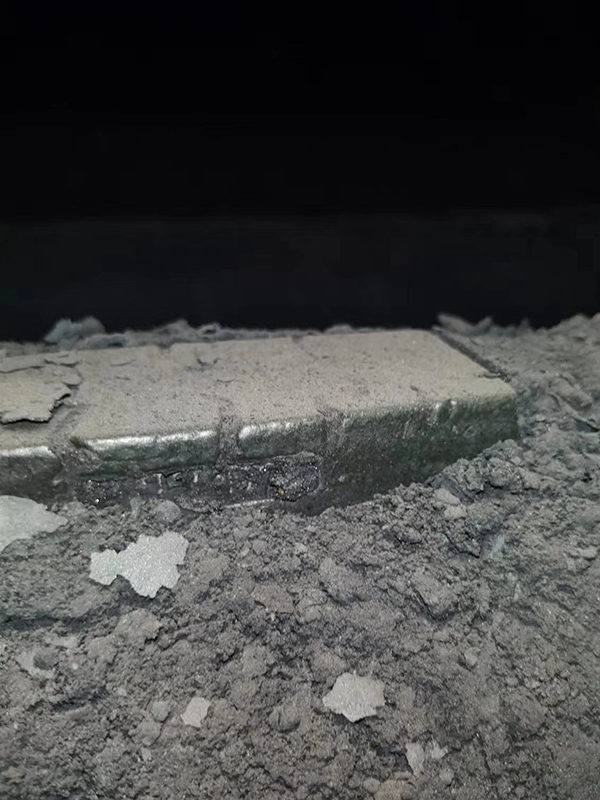


Figure 6 Co50 After One Year of Use (Shansteel Rizhao)
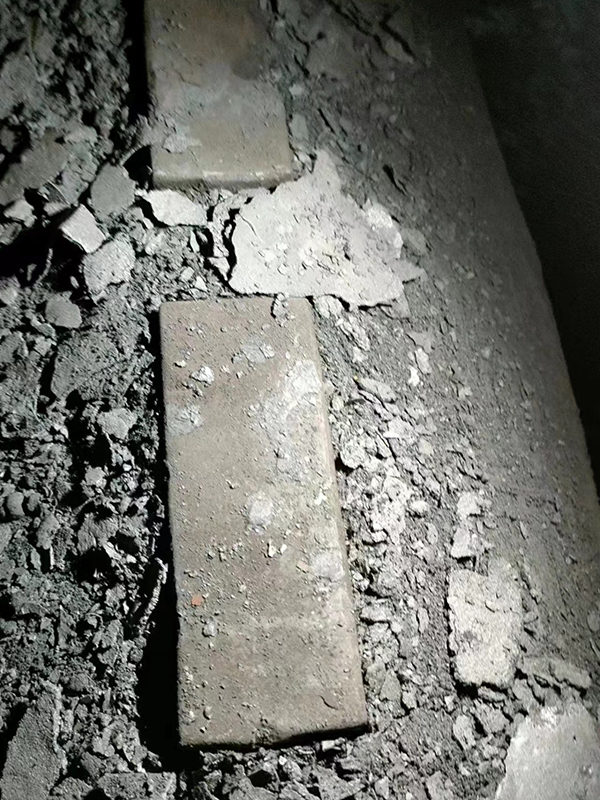
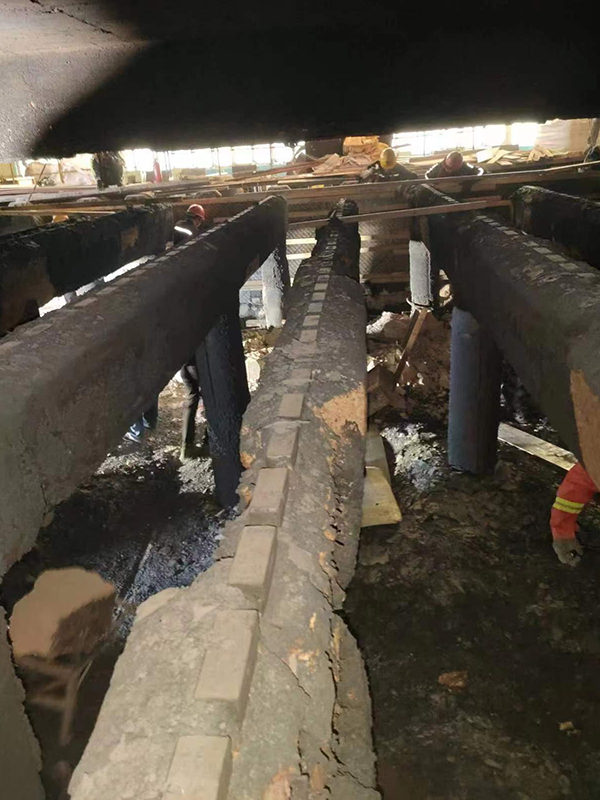


Figure 7 Heating Furnace Spacer Block After One Year of Use (Shansteel Rizhao)
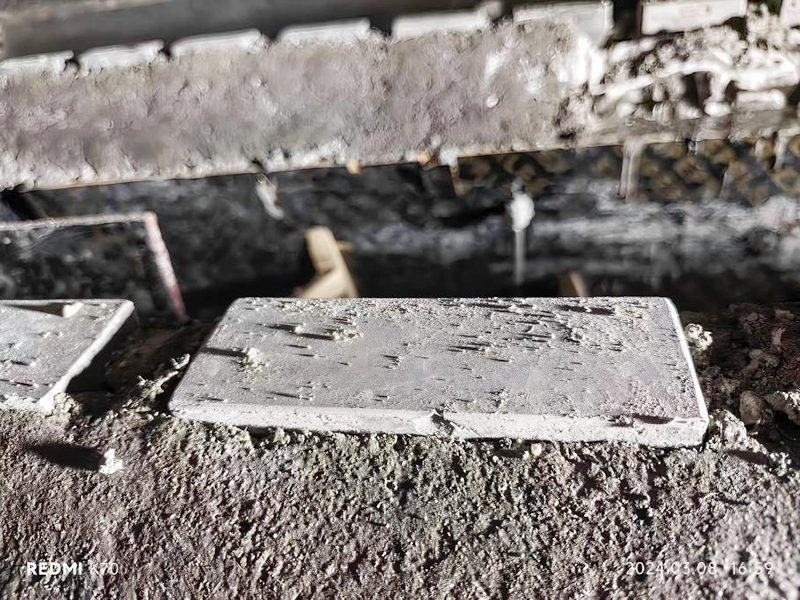
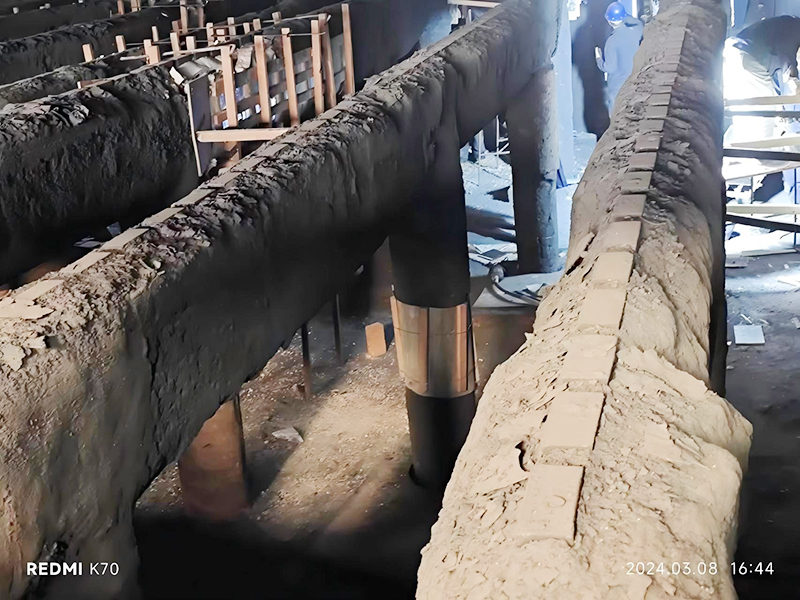
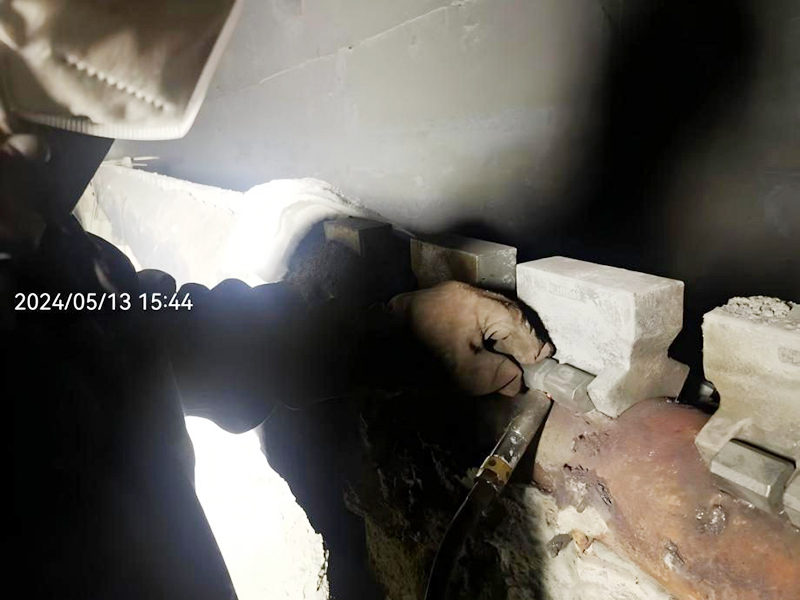



Figure 8 Heating Furnace Spacer Block After Two Years of Use (Shansteel Rizhao)
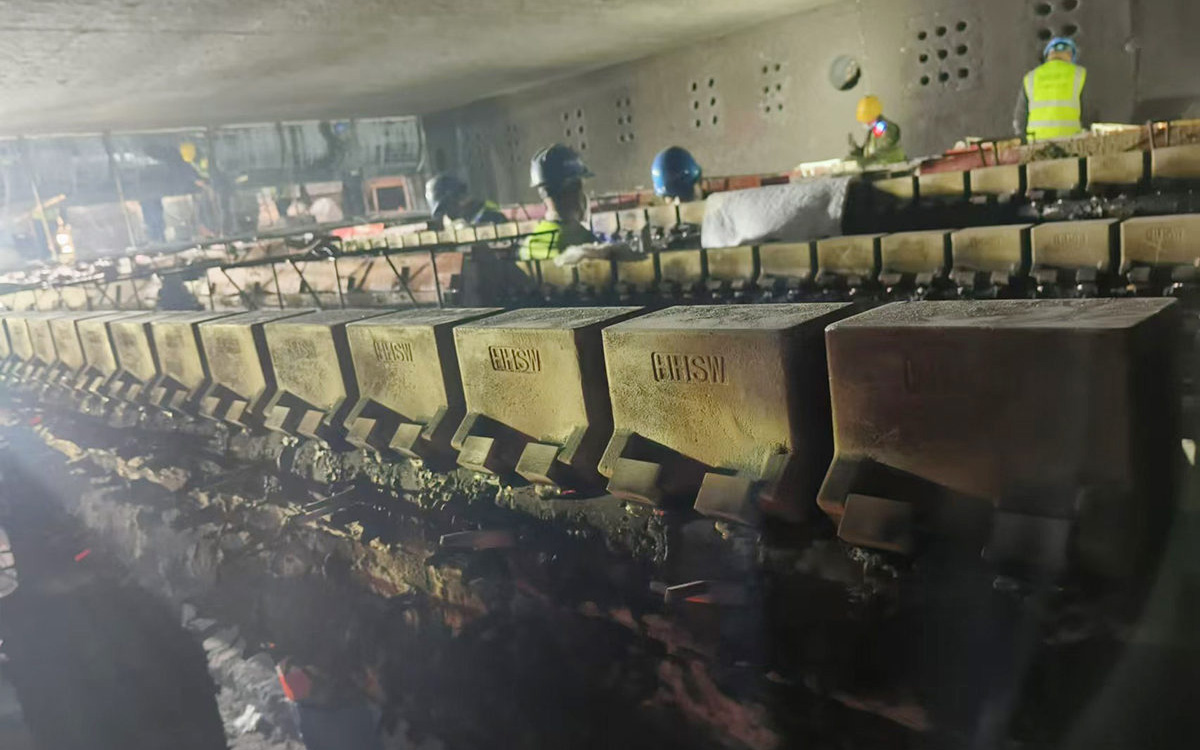
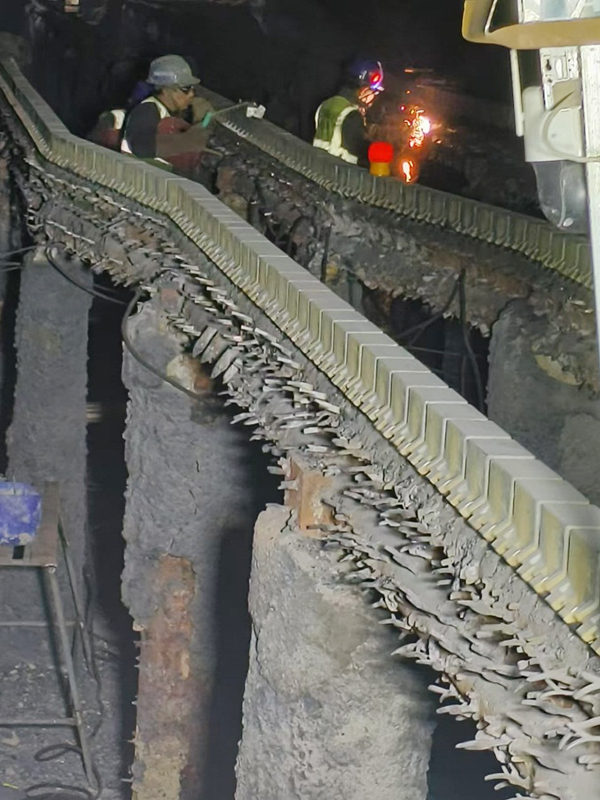


Figure 9 Installation Image of Heating Furnace Spacer Block (Baotou Steel)




